Design and build: appointment
This stage describes the process of making appointments, such as: independent client advisers, members of the consultant team, the employers agent, site inspectors and so on. This stage is likely to be repeated a number of times during the project.
For information about selecting the contractor, see: Design and Build: Tender.
Contents |
[edit] Identifying the need to make appointments.
The client identifies the need to make an appointment. In some cases, existing consultants may identify a requirement and bring this to the attention of the client.
The client may decide they need advice or assistance from independent client advisers or from existing members of the consultant team to help them make the appointment.
The client determines the selection procedure that will be adopted. This might be a process of recommendation, research and interview, open competition (with or without design), selective competition (with or without design), or an existing relationship such as a framework agreement. The client may have to follow a pre-determined procedure if there are in-house rules governing appointments, if they are a local authority or other public body, or if the project will be publicly funded. Such procedures may include assessing whether OJEU procurement rules are likely to apply, which can cause significant delays unless implemented early in the project, as the procedures that must be followed are quite lengthy.
[edit] Agreeing the exact nature of appointments required.
The client agrees the wording of any adverts that are required (such as OJEU adverts) and if appropriate prepares a pre-qualification questionnaire. If it has not already been done, the client prepares documentation describing the nature of the development (such as a strategic brief).
The client defines the schedule of services that will be required, along with selection criteria, form of appointment and contract terms for the appointment. The schedule of services that will be required might include services that are not included on standard forms of appointment, or may be considered 'additional services'. Additional services could include: post-occupancy evaluation services, the use of building information modelling, the preparation of an outline planning application and so on.
The client prepares a formal request for proposals. If design proposals are requested, it is best practice to offer payment to candidates. This ensures that candidates give their full attention to preparing their proposals (which is in the best interests of the client) and ensures that the candidates feel they will be treated fairly by the client.
[edit] Preparing a list of possible candidates.
The client prepares a long list of possible candidates, either from recommendations, existing relationships or expressions of interest received in response to adverts.
The candidates may be required to complete a pre-qualification questionnaire, or there may be some other assessment procedures (such as interviews) that results in the preparation of a short list invited to submit proposals. Such assessments may include evaluating experience and capability, checking professional indemnity insurance, assessing CDM competence, checking references and so on. Short-listed candidates are then invited to submit consultant's proposals in response to the client's request for proposals.
[edit] Selecting the preferred candidate and making the appointment.
The client collates responses to queries from candidates and issues these responses to all candidates.
The client receives and opens the consultant's proposals and makes a record of the fee proposals of each candidate. In some circumstances fee proposals may be submitted in a sealed envelope and opened separately from the rest of the consultant's proposals so that the assessment procedure is not initially prejudiced by the fee (which it may be possible to negotiate down).
The client assesses the consultant's proposals. They may seek advice from existing consultants or independent client advisers to help them do this.
The client then invites the candidates to interview, identifies the preferred candidate(s) and opens negotiations with the preferred candidate(s).
The client appoints the selected candidate and if appropriate arranges a consultant team start-up meeting.
The client informs other candidates that they have been unsuccessful. It is best practice to give clearly thought-out, specific feedback to unsuccessful candidates as they have taken the time to prepare proposals, often for no fee. Candidates greatly appreciate this feedback and will be more likely to express interest in future projects.
Featured articles and news
Scottish Government responds to Grenfell report
As fund for unsafe cladding assessments is launched.
CLC and BSR process map for HRB approvals
One of the initial outputs of their weekly BSR meetings.
Building Safety Levy technical consultation response
Details of the planned levy now due in 2026.
Great British Energy install solar on school and NHS sites
200 schools and 200 NHS sites to get solar systems, as first project of the newly formed government initiative.
600 million for 60,000 more skilled construction workers
Announced by Treasury ahead of the Spring Statement.
The restoration of the novelist’s birthplace in Eastwood.
Life Critical Fire Safety External Wall System LCFS EWS
Breaking down what is meant by this now often used term.
PAC report on the Remediation of Dangerous Cladding
Recommendations on workforce, transparency, support, insurance, funding, fraud and mismanagement.
New towns, expanded settlements and housing delivery
Modular inquiry asks if new towns and expanded settlements are an effective means of delivering housing.
Building Engineering Business Survey Q1 2025
Survey shows growth remains flat as skill shortages and volatile pricing persist.
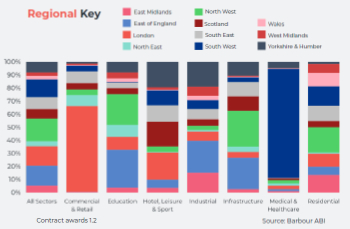
Construction contract awards remain buoyant
Infrastructure up but residential struggles.
Home builders call for suspension of Building Safety Levy
HBF with over 100 home builders write to the Chancellor.
CIOB Apprentice of the Year 2024/2025
CIOB names James Monk a quantity surveyor from Cambridge as the winner.
Warm Homes Plan and existing energy bill support policies
Breaking down what existing policies are and what they do.
Treasury responds to sector submission on Warm Homes
Trade associations call on Government to make good on manifesto pledge for the upgrading of 5 million homes.
A tour through Robotic Installation Systems for Elevators, Innovation Labs, MetaCore and PORT tech.
A dynamic brand built for impact stitched into BSRIA’s building fabric.
BS 9991:2024 and the recently published CLC advisory note
Fire safety in the design, management and use of residential buildings. Code of practice.